Brain
 Brain Of Human
Brain Of Human
This article is concerning options specific to the human brain. For basic info concerning brains, see Brain.
Human brain
- Skull and brain traditional human.svg
- Human brain and os
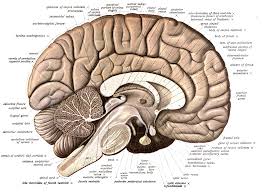
- Cerebral lobes.png
- Cerebral lobes: the lobe (pink), lobe (green) and lobe (blue)
- Details
- Latin neural structure
- System Central systema nervosum
- Artery
- Internal arterial blood vessel arteries, bone arteries
- Vein
- Internal vena, cerebral veins, external veins, basal vein, terminal vein, vein, neural structure veins
- Precursor
- Neural tube
Identifiers
FMA FMA:50801
Anatomical word
Anatomical word
The human brain has an equivalent general structure because the brains of different mammals, however encompasses a a lot of developed cerebral mantle than the other. giant animals like whales and elephants have larger brains in absolute terms, however once measured victimization the encephalization quotient, that compensates for body size, the human brain is sort of doubly as giant because the brain of the bottlenose, and 3 times as giant because the brain of a pongid. a lot of of the enlargement comes from the cerebral mantle, particularly the frontal lobes, that ar related to govt functions like self-control, planning, reasoning, and mentation. The portion of the cerebral mantle dedicated to vision, the cortical region, is additionally greatly enlarged in humans.
The human cerebral mantle could be a thick layer of neural tissue that covers most of the brain. This layer is pleated during a approach that will increase the quantity of surface which will match into the quantity offered. The pattern of folds is comparable across people, though there ar several little variations. The cortex is split into four "lobes", known as the lobe, lobe, lobe, and lobe. (Some classification systems conjointly embody a body structure lobe and treat the insular cortex as a lobe.) at intervals every lobe ar various animal tissue areas, every related to a selected operate, together with vision, control, and language. The left and right sides of the cortex ar broadly speaking similar in form, and most animal tissue aras are replicated on each side. Some areas, though, show sturdy localisation principle, notably aras that are concerned in language. In the majority, the hemisphere is "dominant" for language, with the correct hemisphere enjoying solely a role. There ar different functions, like spatiotemporal reasoning, that the correct hemisphere is typically dominant.
Despite being protected by the thick bones of the os, suspended in bodily fluid, and isolated from the blood by the blood–brain barrier, the human brain is at risk of harm and sickness. the foremost common varieties of physical harm ar closed head injuries like a blow to the top, a stroke, or poisoning by a range of chemicals which will act as neurotoxins. Infection of the brain, tho' serious, is rare attributable to the biological barriers that defend it. The human brain is additionally at risk of chronic disorders, like degenerative disorder, MS, and Alzheimers. variety of psychiatrical conditions, like dementia praecox and depression, ar thought to be related to brain dysfunctions, though the character of such brain anomalies isn't well understood.
Scientifically, the techniques that ar wont to study the human brain disagree in vital ways that from people who ar wont to study the brains of different mammals. On the one hand, invasive techniques like inserting electrodes into the brain, or disabling components of the brain so as to look at the impact on behavior, ar used with non-human species, except for moral reasons, ar usually not performed with humans. On the opposite hand, humans ar the sole subjects WHO will reply to advanced verbal directions. Thus, it's usually potential to use non-invasive techniques like purposeful neuroimaging or encephalogram recording a lot of profitably with humans than with non-humans. moreover, a number of the foremost vital topics, like language, will hardly be studied in the least except in humans. In several cases, human and non-human studies type essential enhances to every different. Individual brain cells (except wherever tissue samples ar taken for diagnostic assay for suspected brain tumors) will solely be studied in non-humans; advanced psychological feature tasks will solely be studied in humans. Combining the 2 sources of knowledge to yield a whole purposeful understanding of the human brain is associate in progress challenge for neurobiology.

Comments